DB App Eyetracking
UX Research
Project Overview
Objective
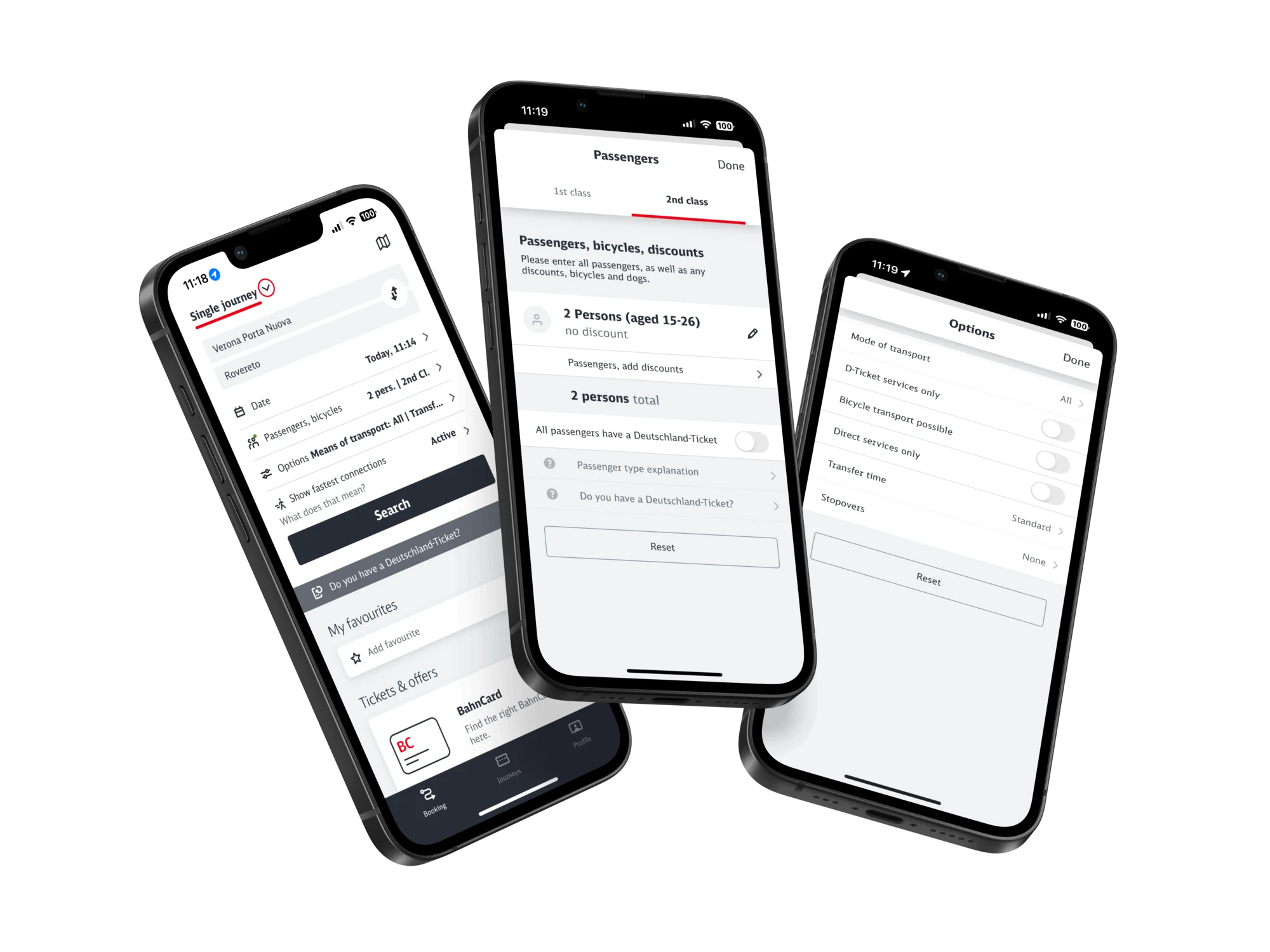
This project was a collaborative university research study aimed at evaluating the usability of the Deutsche Bahn (DB) app, specifically how easily users could navigate and complete common tasks when booking a ticket. Given our initial impression that the app was not user-friendly, we wanted to test this assumption through usability testing and eye-tracking technology.
Info
Team: Team of 5 UX Researchers
Duration: Two Months
Tools: Figma, Eye-tracking Glasses
Type: University Exchange Project
Goals
- Identify navigation pain points - Pinpoint where users struggle to locate key booking features.
- Measure usability with data - Use eye-tracking and surveys to capture both quantitative and qualitative insights.
- Generate actionable recommendations - Provide evidence-based suggestions to improve the app’s booking flow and feature discoverability.
Challenges
- Unfamiliar user base - Recruiting international students unfamiliar with the app to remove bias while ensuring tasks were still realistic.
- Scenario design - Crafting booking scenarios that tested core functions without over-directing participants.
- Survey neutrality - Designing post-test survey questions that gathered valuable insights without leading or biasing responses.
- Time constraints - Completing participant recruitment, testing, analysis, and reporting within a tight academic timeline.
01 - Discover
As part of a collaborative university research study, we set out to evaluate the usability of the Deutsche Bahn (DB) app, focusing on how easily users could navigate and complete common booking tasks. Our initial impression was that the app was not user-friendly, so we aimed to test this assumption using usability testing combined with eye-tracking technology.
To avoid bias from learned behaviour, we specifically recruited international students unfamiliar with the app. This allowed us to observe natural navigation patterns and identify friction points without prior experience influencing results.

02 - Define
The project goals were to:
- Identify navigation pain points within the DB app.
- Use eye-tracking and survey data to measure usability.
- Provide data-driven insights for potential UX improvements.
A key challenge was determining whether new users could locate and use essential booking features without guidance - particularly the “Search Options” tool, which is critical for refining ticket searches.

03 - Develop
We began by creating user personas to represent our test group and designed three realistic travel scenarios targeting common booking behaviours. These scenarios were carefully crafted to test core app functions, including searching for tickets, refining search options, and selecting specific train types.
Participants wore eye-tracking glasses during testing, allowing us to capture heat maps and gaze patterns. After each session, participants completed a post-test survey to provide qualitative feedback on their experience. This required careful question design to avoid leading participants or introducing bias while still eliciting actionable insights. Testing and refining the survey in advance ensured that results reflected genuine user perceptions rather than prompted answers.
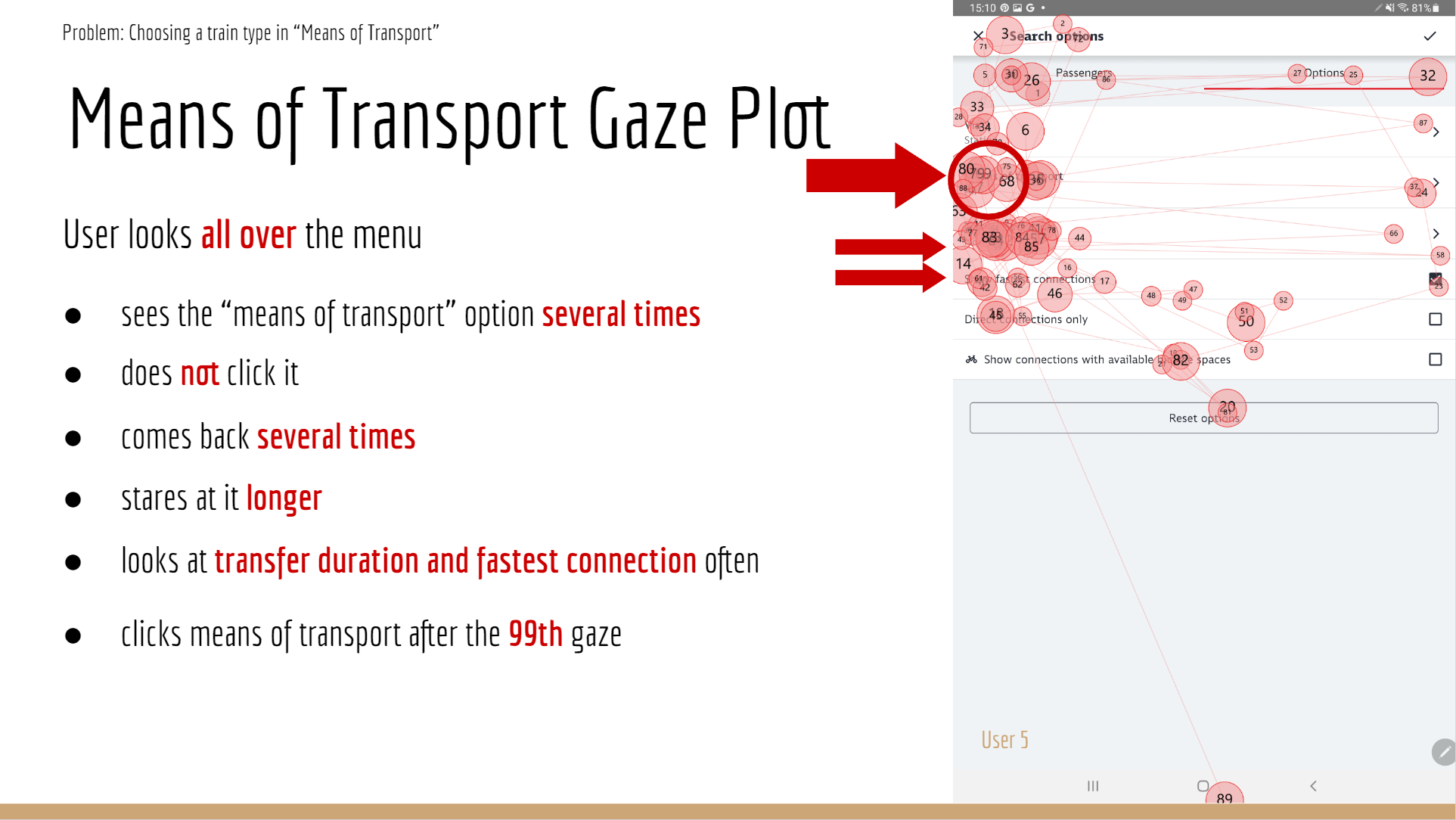
Data analysis revealed a significant usability issue: the “Search Options” feature was often overlooked or discovered only after excessive searching, in one case, after the participant’s 99th gaze. This made filtering for tickets (such as the 9-Euro ticket) unnecessarily difficult, even when users were highly motivated.
04 - Deliver
The study produced clear, evidence-based insights into the app’s navigation shortcomings. The key finding was the difficulty users had locating and using the “Search Options” feature, a critical function for filtering ticket results.
We recommended that Deutsche Bahn consider UI adjustments to make this tool more visible and intuitive, as poor discoverability directly impacted the speed and ease of booking. These insights could be used to create redesign mock-ups and tested through A/B experiments to measure improvements in task completion time and user satisfaction.

05 - Reflection
This project reinforced the importance of user-centred design in driving both usability and business outcomes. The DB app’s current design risks frustrating new users and reducing engagement, potentially impacting ticket sales.
If extended, the research could test additional app features, validate proposed redesigns, and explore how small UI changes could streamline navigation. For me, this study also underscored the value of combining quantitative eye-tracking data with qualitative user feedback to build a comprehensive understanding of UX challenges.